How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand, spanning leisure pursuits to professional applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll explore various flight modes, camera settings, and maintenance procedures, ensuring you’re equipped to handle your drone with confidence and expertise.
Mastering drone piloting involves understanding not just the mechanics but also the safety protocols and legal frameworks governing their use. We’ll cover essential pre-flight checklists, navigate the nuances of drone controls, and delve into optimizing camera settings for breathtaking aerial photography and videography. Through practical examples and clear explanations, this guide aims to transform you from a novice into a proficient drone operator.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various components, verifying system functionality, and understanding emergency procedures. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents or data loss.
Pre-flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection covers several key areas. First, you must check the drone’s battery level. Ensure it’s adequately charged and in good condition, free from any visible damage or swelling. Next, carefully examine the propellers for any cracks, bends, or other signs of wear and tear. Damaged propellers can cause instability and crashes.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of the regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide on all aspects of flight, including pre-flight and in-flight procedures, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Learning how to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for responsible operation.
Finally, confirm a strong GPS signal is established. A weak signal can impair flight stability and autonomous features.
Pre-flight Checklist, How to operate a drone
The following table provides a structured approach to pre-flight checks:
| Item | Check | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check voltage and remaining flight time | ||
| Propeller Condition | Inspect for cracks, bends, or damage | Replace damaged propellers | |
| GPS Signal Strength | Verify sufficient satellites are acquired | Ensure signal is strong and stable | |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and proper calibration | ||
| Camera Function | Test camera operation and image quality | ||
| Flight Controller | Ensure all systems are functioning correctly | ||
| Radio Link | Verify stable connection between the controller and drone | ||
| Surrounding Environment | Assess wind conditions, obstacles, and airspace restrictions | Avoid flying in high winds or near obstacles |
Safe Launching and Landing Procedures

Launching and landing a drone safely requires a methodical approach. Find a clear, open area, free from obstacles and people. Before launching, carefully position the drone and gently power it on. After a successful GPS lock, initiate takeoff using the designated control, ensuring a slow and steady ascent. For landing, initiate the landing sequence through the controller, guiding the drone smoothly to the ground.
Always maintain visual contact with the drone throughout the entire process.
Emergency Procedures
Loss of signal and low battery are common emergencies. In case of signal loss, the drone’s Return-to-Home (RTH) function should automatically engage, returning it to the launch point. If the RTH fails, you may need to manually attempt to regain control or initiate an emergency landing. Low battery situations require immediate action. Land the drone as soon as possible to avoid a sudden power failure mid-flight.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning how to handle the controls effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and its implications.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. These controls allow you to maneuver the drone in three-dimensional space, capturing the desired footage or completing the intended task. Different interfaces offer varying levels of control and precision.
Basic Drone Controls
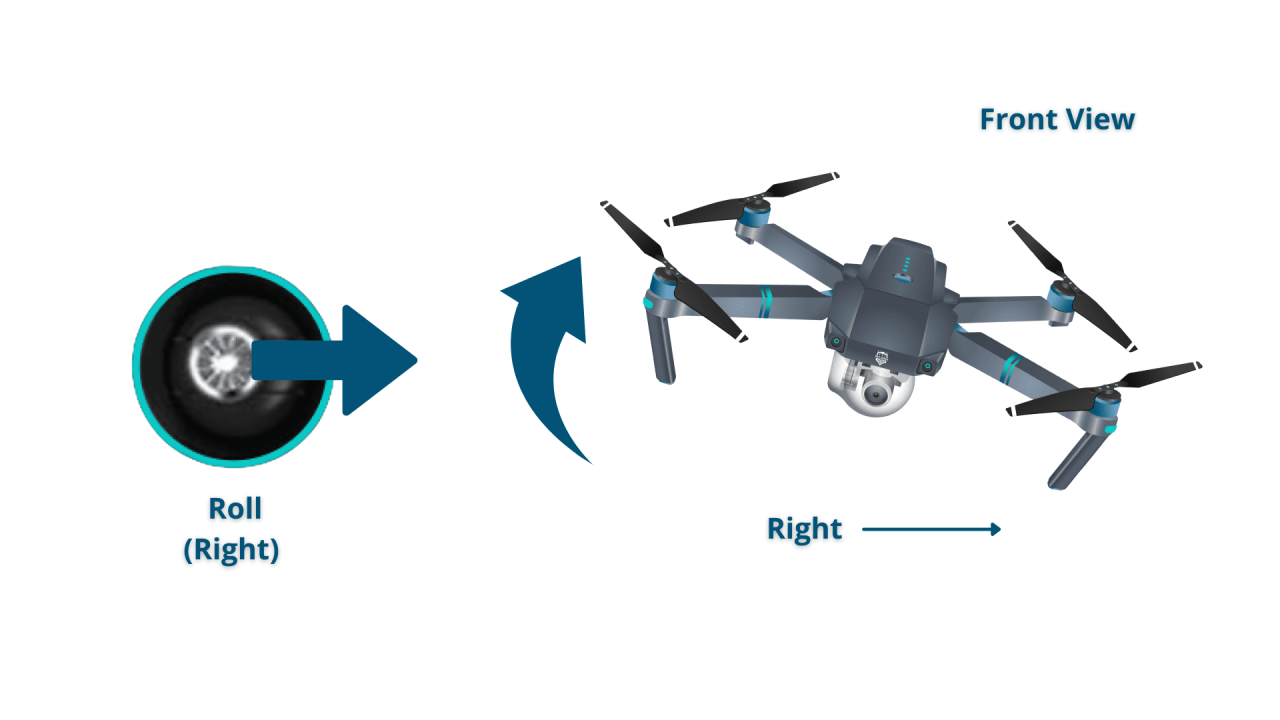
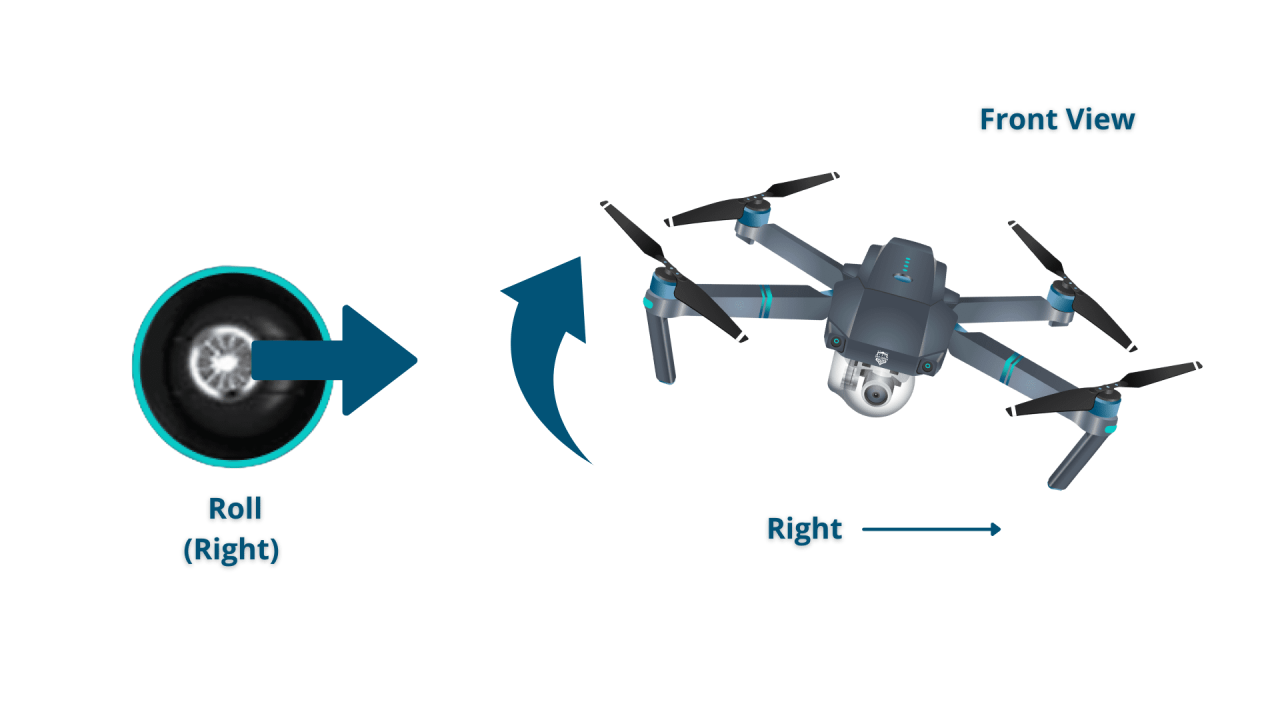
Most drones utilize a control scheme involving four primary axes: throttle (up/down), yaw (rotation), pitch (forward/backward), and roll (left/right). These controls work in conjunction to allow for precise maneuvering. Throttle controls altitude, yaw rotates the drone around its vertical axis, pitch controls the drone’s forward and backward movement, and roll controls side-to-side movement.
Drone Control Interfaces
Two common interfaces are joysticks and touchscreens. Joysticks provide more precise and responsive control, especially for quick maneuvers, while touchscreens offer a more intuitive and user-friendly experience, particularly for beginners. The choice depends on personal preference and the complexity of the intended flight operation.
GPS-Assisted Flight and Waypoint Navigation
GPS enables autonomous flight and waypoint navigation. By setting waypoints on a map within the drone’s software, the drone can autonomously navigate a pre-defined route. This feature is incredibly useful for tasks requiring repetitive or complex flight paths, such as aerial photography or surveying.
Smooth and Precise Drone Maneuvering
Smooth and precise maneuvering requires practice and a gentle touch on the controls. Avoid abrupt movements, and use small, incremental adjustments to control the drone’s position and orientation. Learning to anticipate the drone’s response is crucial for maintaining control and avoiding accidents.
Flight Modes and Settings
Drones typically offer various flight modes tailored to different skill levels and flight scenarios. Understanding these modes and adjusting settings is vital for optimizing flight performance and safety.
Drone Flight Modes
Beginner mode limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, making it ideal for novice pilots. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers for experienced users. GPS mode utilizes the drone’s GPS system for enhanced stability and features like Return-to-Home (RTH).
Adjusting Drone Settings

Settings such as altitude limits, RTH parameters, and camera configurations can be adjusted to suit specific needs. Altitude limits restrict the maximum flight height, enhancing safety. RTH ensures the drone returns to its starting point in case of signal loss. Camera settings allow control over exposure, focus, and other image capture parameters.
Flight Mode Comparison
The following table compares different flight modes and their suitability for various tasks:
| Flight Mode | Description | Suitable for | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness | Beginners, training | Safe, easy to learn | Limited maneuverability |
| Sport Mode | Unrestricted speed and responsiveness | Experienced pilots | High maneuverability | Requires skill, higher risk |
| GPS Mode | Utilizes GPS for stability and RTH | Most tasks | Stable flight, automatic return | Requires GPS signal |
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of many drones, enabling high-quality aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is essential for capturing stunning visuals.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture control exposure and image quality. ISO affects sensitivity to light, shutter speed determines motion blur, and aperture influences depth of field. Adjusting these settings based on lighting conditions and desired effects is crucial for optimal image capture.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Capturing high-quality media involves understanding the interplay between camera settings, lighting, and composition. Shoot in well-lit conditions, use a tripod or gimbal for stability (if applicable), and experiment with different settings to achieve your desired look. Always review your footage to ensure the quality meets your expectations.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Different camera angles and perspectives can significantly impact the visual appeal of your shots. Experiment with various angles, such as high-angle shots for a sweeping overview or low-angle shots for a dramatic perspective. Consider the subject and the desired mood when selecting camera angles.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
The following table illustrates how various camera settings affect image quality:
| Setting | Effect on Image |
|---|---|
| High ISO | Increased noise, reduced detail |
| Low ISO | Reduced noise, sharper image |
| Fast Shutter Speed | Freezes motion, reduces blur |
| Slow Shutter Speed | Creates motion blur, can be artistic |
| Wide Aperture | Shallow depth of field, blurred background |
| Narrow Aperture | Deep depth of field, everything in focus |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are vital for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This involves routine checks, cleaning, and addressing potential issues promptly.
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance includes cleaning propellers, inspecting for physical damage, and checking all connections and components for wear and tear. Clean propellers improve efficiency and reduce the risk of imbalance. Regular inspections help identify potential problems before they escalate.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Common drone problems include battery issues (low charge, swelling), motor malfunctions (unresponsive motors, unusual noises), and GPS signal loss. Battery issues may require replacing the battery or charging it properly. Motor problems might indicate a mechanical failure or wiring issue. GPS signal loss can be addressed by moving to an open area with better satellite reception.
Essential Maintenance Tools
A basic drone maintenance kit should include a small screwdriver set, a cleaning brush, a multimeter for checking battery voltage, and replacement propellers. These tools allow for basic repairs and maintenance tasks.
Proper Drone Storage
Proper storage protects the drone from damage and extends its lifespan. Store the drone in a clean, dry environment, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use a protective case or bag to prevent scratches and damage during transportation.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone requires adherence to local laws and regulations. Understanding these rules is crucial for legal and responsible drone operation.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Laws and regulations vary by location. They often address airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. It is essential to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before flying.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones
Certain areas, such as airports, military bases, and densely populated areas, are designated as restricted airspace or no-fly zones. Flying in these areas is illegal and potentially dangerous. Utilize online resources to identify restricted airspace before flight planning.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses to operate a drone commercially or for specific activities. Check with your local aviation authority for details.
Resources for Drone Regulations
Several online resources provide up-to-date information on drone regulations. These include websites of national aviation authorities and specialized drone websites. Always consult these resources before each flight to ensure compliance.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Beyond basic flight, advanced techniques unlock creative possibilities and enhance drone capabilities for various applications.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers include circling, tracking moving objects, and performing aerial acrobatics. These techniques require significant practice and skill, and should only be attempted in safe, controlled environments.
Specialized Drone Accessories
Accessories such as gimbal stabilizers and external cameras enhance drone capabilities. Gimbal stabilizers provide smooth, stable footage, even during complex maneuvers. External cameras offer different perspectives and functionalities, expanding creative options.
Capturing Cinematic Footage
Capturing cinematic footage involves careful planning, smooth camera movements, and creative shot composition. Using advanced maneuvers, different camera angles, and appropriate editing techniques can create visually stunning results.
Drone Applications
Drones find applications in various fields, including aerial photography, videography, inspections, and deliveries. Each application requires specific skills, knowledge, and equipment tailored to the task at hand.
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical skill, adherence to safety regulations, and a keen understanding of your equipment. This guide has provided a foundational framework for responsible drone piloting, covering pre-flight preparations, flight controls, camera operation, maintenance, and legal compliance. By diligently practicing the techniques Artikeld and staying updated on relevant regulations, you can confidently explore the exciting world of aerial flight, capturing stunning visuals and undertaking various tasks with your drone.
Quick FAQs: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight speed). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight to maintain control.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.